Most scalp conditions lead to hair loss or some type of skin rash. Many are hereditary. Chronic conditions, malnutrition, or infection can also cause scalp conditions. The treatment and your outlook depend on the cause.
Many conditions can affect your scalp, ranging from chronic health issues to environmental exposures, infections, and parasites. Identifying the cause of your scalp condition is crucial to finding and effectively treating it.
Working through the process of diagnosis and treatment can be stressful, and finding a healthcare professional who knows about scalp conditions can be extremely helpful on your journey.
Read on to view images of scalp conditions, their causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
There are many different types of scalp conditions, resulting from various causes.
Here are 12 possible scalp conditions, what they look like, and how to tell if you may have one of them.
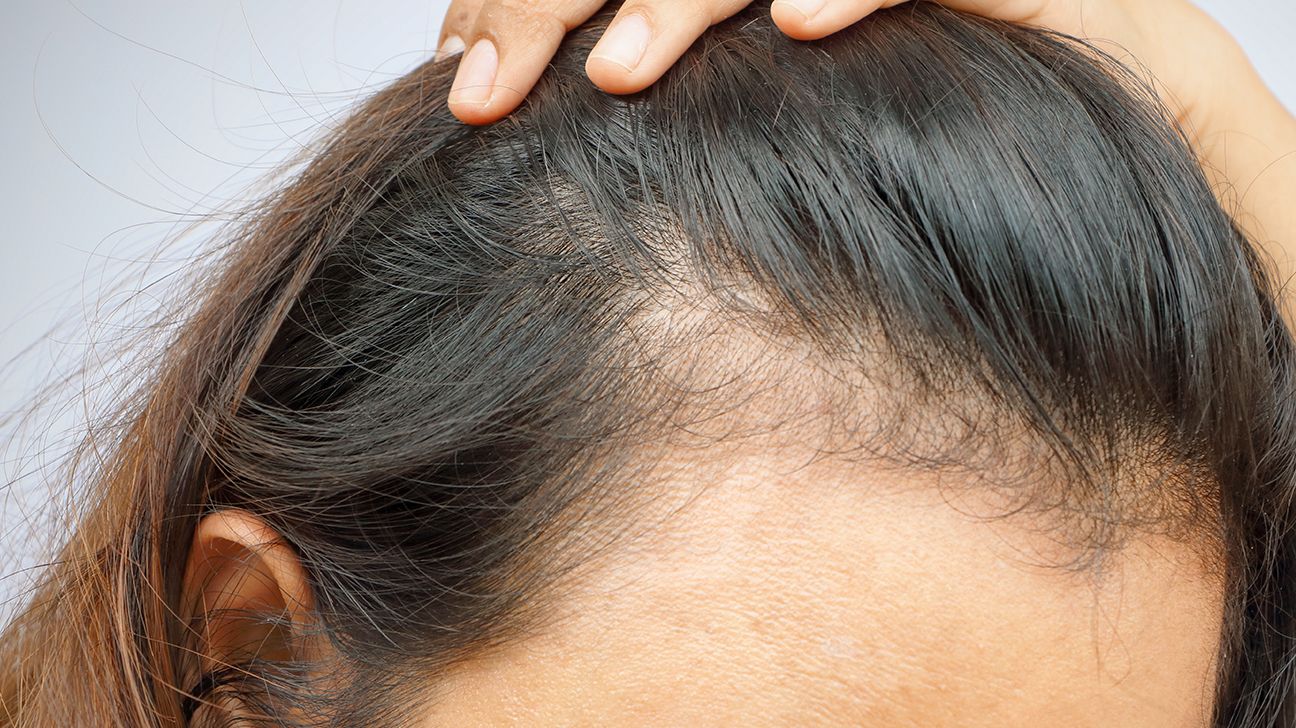
One of the most common types of scalp conditions involves hair loss or damage. This can range from a complete loss of hair to easy breakages or small patches of hair loss:
- You may notice a large amount of hair in the drain after you wash your hair.
- You may notice a large amount of hair in the drain after you wash your hair.
- You may find clumps of hair in your brush.
- Hair that falls out easily with gentle pulling may be a sign of hair loss.
- Thinning patches of hair may also indicate hair loss.
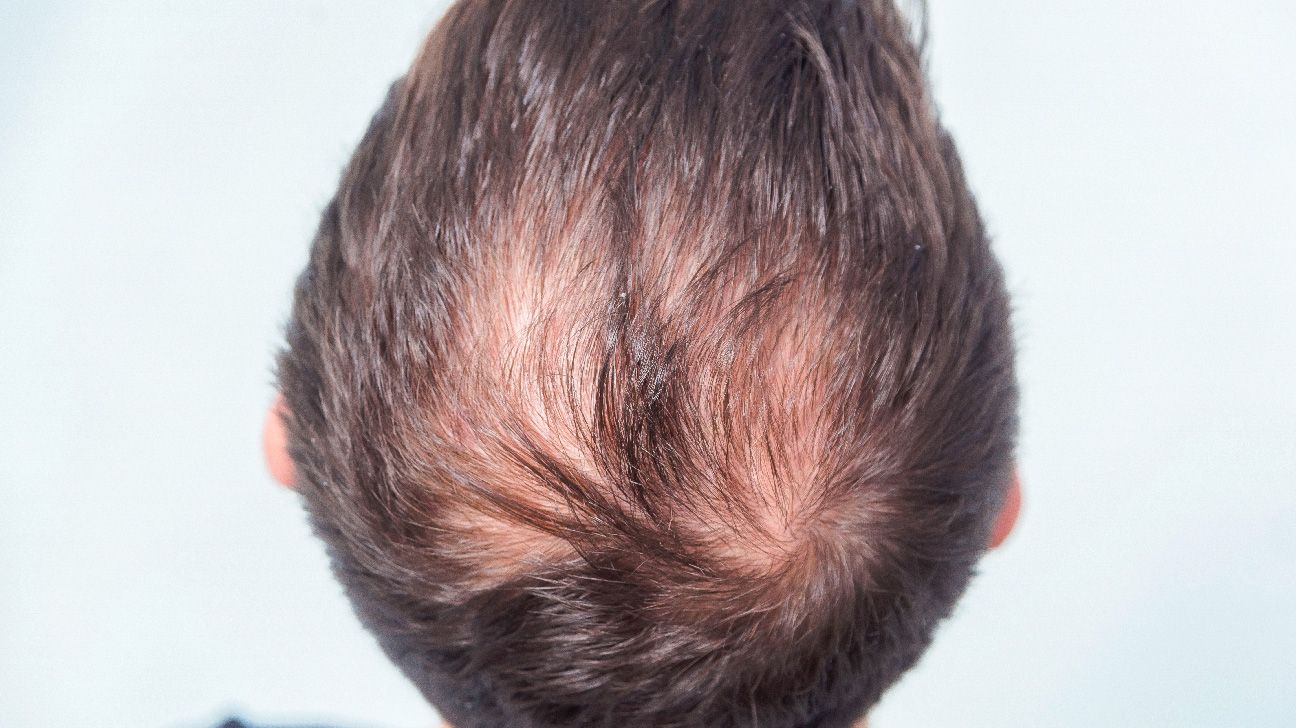
- Male pattern baldness is common in men and occurs because of genetics and male sex hormones.
- Hair loss at the temples of the head is a possible sign of male pattern baldness.
- With male pattern baldness, you may develop a bald spot or hairline that recedes to form an “M” shape.
- This common and self-limiting skin condition is seen in infants and young children between the ages of 3 weeks and 12 months.
- It’s painless and non-itchy.
- Yellowish, greasy scales appear on the scalp and forehead that flake off.
- It usually doesn’t require medical treatment and will go away on its own in 6 months.
- Psoriasis typically results in scaly, silvery, sharply defined skin patches.
- It’s commonly located on the scalp, elbows, knees, and lower back.
- It may be itchy or asymptomatic (producing or showing no symptoms).
- This is a fungal infection that affects your scalp and hair shafts is a also called ringworm of the scalp even though it is not caused by a worm.
- Itchy, flaky patches appear on the scalp.
- Brittle hair, hair loss, scalp pain, low fever, swollen lymph nodes are other possible symptoms.
- Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is caused by an inappropriate immune response to the thyroid gland.
- Low thyroid hormone causes symptoms of decreased metabolism.
- Symptoms include thinning hair, sluggishness, fatigue, and hoarseness.
- Other symptoms include constipation, high cholesterol, depression, and lower body muscle weakness.
- Alopecia areata is a chronic autoimmune disorder characterized by patchy hair loss.
- It causes the immune system to mistakenly attack hair follicles, leading to hair loss.
- Hair loss occurs randomly all over the scalp or other parts of the body in small, smooth, quarter-sized patches that may combine into larger areas and may not be permanent.
- Hair may grow back slowly or fall out again after regrowth.
- A louse is about the size of a sesame seed. Both lice and their eggs (nits) may be visible in the hair.
- Extreme scalp itchiness can be caused by an allergic reaction to louse bites.
- Sores may appear on your scalp from scratching.
- You may feel like something is crawling on your scalp.
Image credit: © Bittencourt MJS, et al. (2015). Trichoscopy as a diagnostic tool in trichorrhexis invaginata. Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia. CC BY-NC.
- Bamboo hair is a defect in the structure of hair that results in brittle or fragile hair strands that break easily.
- It leads to sparse hair growth and eyelash or eyebrow loss.
- Hair strands have a dry, knotty appearance.
- It’s a common symptom of Netherton’s syndrome.
- This uncommon disorder may affect the skin, oral cavity, scalp, nails, genitals, or esophagus.
- Lesions develop and spread over the course of several weeks or a few months.
- Itchy, purplish-colored lesions or bumps with flat tops appear that may be covered by thin, white lines.
- Lacy-white lesions in the mouth may occur, which can be painful or cause a burning sensation.
- Blisters that burst and become scabby are another possible symptom.
- This autoimmune disease is characterized by changes in the texture and appearance of the skin, resulting from increased collagen production.
- Skin thickening and shiny areas develop around the mouth, nose, fingers, and other bony areas.
- Symptoms include swollen fingers, small, dilated blood vessels under the skin’s surface, calcium deposits under the skin, and difficulty swallowing.
- Spasms of the blood vessels in the fingers and toes cause these digits to turn white or blue in the cold.
- This disease occurs when the immune cells within a bone marrow graft don’t match the recipient’s cells, causing the donor cells to attack the recipient’s cells.
- The most commonly involved organs are the skin, gastrointestinal tract, and liver.
- It can occur within 100 days after transplantation (acute GVHD) or over a longer period of time (chronic GVHD).
- A sunburn-like, itchy, painful rash appears that can cover up to 50% of the body.
- Nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramping, diarrhea, bloody stools, and dark urine are other possible symptoms.
The symptoms of scalp conditions depend on the exact condition, but they include:
You may experience other symptoms that are characteristic of particular conditions and not necessarily related to the scalp.
Treatment for scalp conditions varies depending on the diagnosis. Treatment options may include:
- Prescription medications: These are available to help treat hair loss. Medications can also treat autoimmune disorders and hormone disorders.
- Surgical implants of hair transplants: These surgical options can replace lost hair while you treat the underlying cause of hair loss, if appropriate.
- Supplements or dietary changes: These can correct nutritional deficiencies. For example, celiac disease can be treated by avoiding gluten in your diet.
- Medicated ointments and washes: These may kill fungi or certain insects, which can help cure ringworm and lice.
- Medicated shampoos: These may help treat seborrheic eczema and cradle cap.
Finding support
Here are a few organizations that may offer support:
The Women’s Hair Loss Project: A place for women facing hair loss can gather and find support.
National Alopecia Areata Foundation (NAAF): Providing support and resources for individuals with alopecia areata.
The Bald Truth (radio program): A place to discuss the feelings surrounding hair loss.
The outlook for many individuals with scalp conditions is generally positive.
Medications that slow hair growth or regrow hair are somewhat successful, and wigs are always an option if medications are not effective in treating the scalp condition. You can receive treatment to eliminate scalp conditions caused by infections.
Although some other scalp conditions aren’t curable, treatment can successfully help you manage your symptoms.
Many conditions can affect your scalp, ranging from chronic health issues to environmental exposures, infections, and parasites. Identifying the cause of your scalp condition is crucial to finding and effectively treating it.
Having a scalp condition can be stressful and emotionally challenging. Finding a healthcare professional who understands conditions affecting the scalp is helpful. You may also want to find support from others who have a scalp condition. Ask your healthcare professional if there are any support groups available online or in your local area.
Effective treatment options are available for various types of scalp conditions. Your healthcare professional can help identify the cause of your scalp condition and suggest ways to improve it.




